faasd - a lightweight & portable faas engine
faasd is OpenFaaS reimagined, but without the cost and complexity of Kubernetes. It runs on a single host with very modest requirements, making it fast and easy to manage. Under the hood it uses containerd and Container Networking Interface (CNI) along with the same core OpenFaaS components from the main project.
When should you use faasd over OpenFaaS on Kubernetes?
- You have a cost sensitive project - run faasd on a 5-10 USD VPS or on your Raspberry Pi
- When you just need a few functions or microservices, without the cost of a cluster
- When you don't have the bandwidth to learn or manage Kubernetes
- To deploy embedded apps in IoT and edge use-cases
- To shrink-wrap applications for use with a customer or client
faasd does not create the same maintenance burden you'll find with maintaining, upgrading, and securing a Kubernetes cluster. You can deploy it and walk away, in the worst case, just deploy a new VM and deploy your functions again.
About faasd
- is a single Golang binary
- uses the same core components and ecosystem of OpenFaaS
- is multi-arch, so works on Intel
x86_64and ARM out the box - can be set-up and left alone to run your applications
Demo of faasd running in KVM
Try faasd for the first time
faasd is OpenFaaS, so many things you read in the docs or in blog posts will work the same way.
Use-cases and tutorials:
- Deploy via GitHub Actions
- Scrape and automate websites with Puppeteer
- Serverless Node.js that you can run anywhere
- Build a Flask microservice with OpenFaaS
Additional resources:
- For reference: OpenFaaS docs
- For use-cases and tutorials: OpenFaaS blog
- For self-paced learning: OpenFaaS workshop
Deploy faasd
The easiest way to deploy faasd is with cloud-init, we give several examples below, and post IaaS platforms will accept "user-data" pasted into their UI, or via their API.
For trying out fasad on MacOS or Windows, we recommend using multipass.
If you don't use cloud-init, or have already created your Linux server you can use the installation script as per below:
git clone https://github.com/openfaas/faasd
cd faasd
./hack/install.sh
This approach also works for Raspberry Pi
It's recommended that you do not install Docker on the same host as faasd, since 1) they may both use different versions of containerd and 2) docker's networking rules can disrupt faasd's networking. When using faasd - make your faasd server a faasd server, and build container image on your laptop or in a CI pipeline.
Run locally on MacOS, Linux, or Windows with multipass
DigitalOcean tutorial with Terraform and TLS
The terraform can be adapted for any IaaS provider:
See also: Build a Serverless appliance with faasd and cloud-init
Get started on armhf / Raspberry Pi
You can run this tutorial on your Raspberry Pi, or adapt the steps for a regular Linux VM/VPS host.
Terraform for DigitalOcean
Automate everything within < 60 seconds and get a public URL and IP address back. Customise as required, or adapt to your preferred cloud such as AWS EC2.
faasd handbook - everything you need to know to run functions without Kubernetes (early access)
faasd is a portable, and open source serverless engine. It runs a number of core services for its REST API, for background processing, and for metrics. The project schedules functions with containerd directly, and supports scale to and from zero, but without the need for clustering or Kubernetes.
It makes for a quick and easy way to start hosting APIs and websites, benefiting from containers and cloud native technology without having to manage Kubernetes, or pay significant hosting costs.
This handbook is written for those deploying faasd to self-hosted or cloud infrastructure. Whilst OpenFaaS has reference documentation, here we focus on everything you need to know about faasd itself.
Topics include:
- Should you deploy to a VPS or Raspberry Pi?
- Deploying your server with bash, cloud-init or terraform
- Using a private container registry
- Building your first function, and customising templates
- Monitoring your functions with Grafana and Prometheus
- Scheduling invocations and background jobs
- Tuning timeouts, parallelism, running tasks in the background
- Upgrading faasd
- Setting memory limits for functions
- Exposing the core services like Prometheus and NATS
faasd users can upgrade to Kubernetes when the need presents itself and can bring their functions with them.
Finding logs
Logs for functions
You can view the logs of functions using journalctl:
journalctl -t openfaas-fn:FUNCTION_NAME
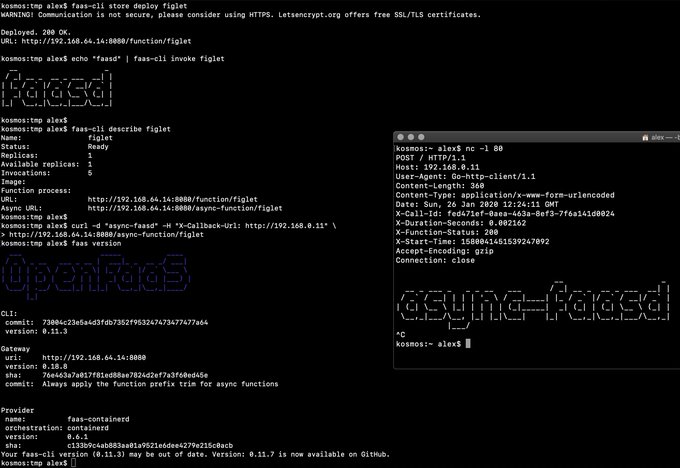
faas-cli store deploy figlet
journalctl -t openfaas-fn:figlet -f &
echo logs | faas-cli invoke figlet
What does faasd deploy?
- faasd - itself, and its faas-provider for containerd - CRUD for functions and services, implements the OpenFaaS REST API
- Prometheus - for monitoring of services, metrics, scaling and dashboards
- OpenFaaS Gateway - the UI portal, CLI, and other OpenFaaS tooling can talk to this.
- OpenFaaS queue-worker for NATS - run your invocations in the background without adding any code. See also: asynchronous invocations
- NATS for asynchronous processing and queues
You'll also need:
You can use the standard faas-cli along with pre-packaged functions from the Function Store, or build your own using any OpenFaaS template.
Instructions for hacking on faasd itself
See here for manual / developer instructions
Getting help
faasd handbook
"Serverless For Everyone Else" is the complete guide and documentation for faasd. If you're looking for how to do something, it's likely that the book covers it.
Reference docs for Kubernetes
The OpenFaaS docs provide a wealth of information for OpenFaaS on Kubernetes, and are likely to be useful for you, even using faasd.
Function and template store
For community functions see faas-cli store --help
For templates built by the community see: faas-cli template store list, you can also use the dockerfile template if you just want to migrate an existing service without the benefits of using a template.
Training and courses
LinuxFoundation training course
The founder of faasd and OpenFaaS has written a training course for the LinuxFoundation which also covers how to use OpenFaaS on Kubernetes. Much of the same concepts can be applied to faasd, and the course is free:
Community workshop
The OpenFaaS workshop is a set of 12 self-paced labs and provides a great starting point for learning the features of openfaas. Not all features will be available or usable with faasd.
Community support
Commercial users and solo business owners should become OpenFaaS GitHub Sponsors to receive regular email updates on changes, tutorials and new features.
If you are learning faasd, or want to share your use-case, you can join the OpenFaaS Slack community.
Backlog, features and known issues
For completed features, WIP and upcoming roadmap see:
See ROADMAP.md